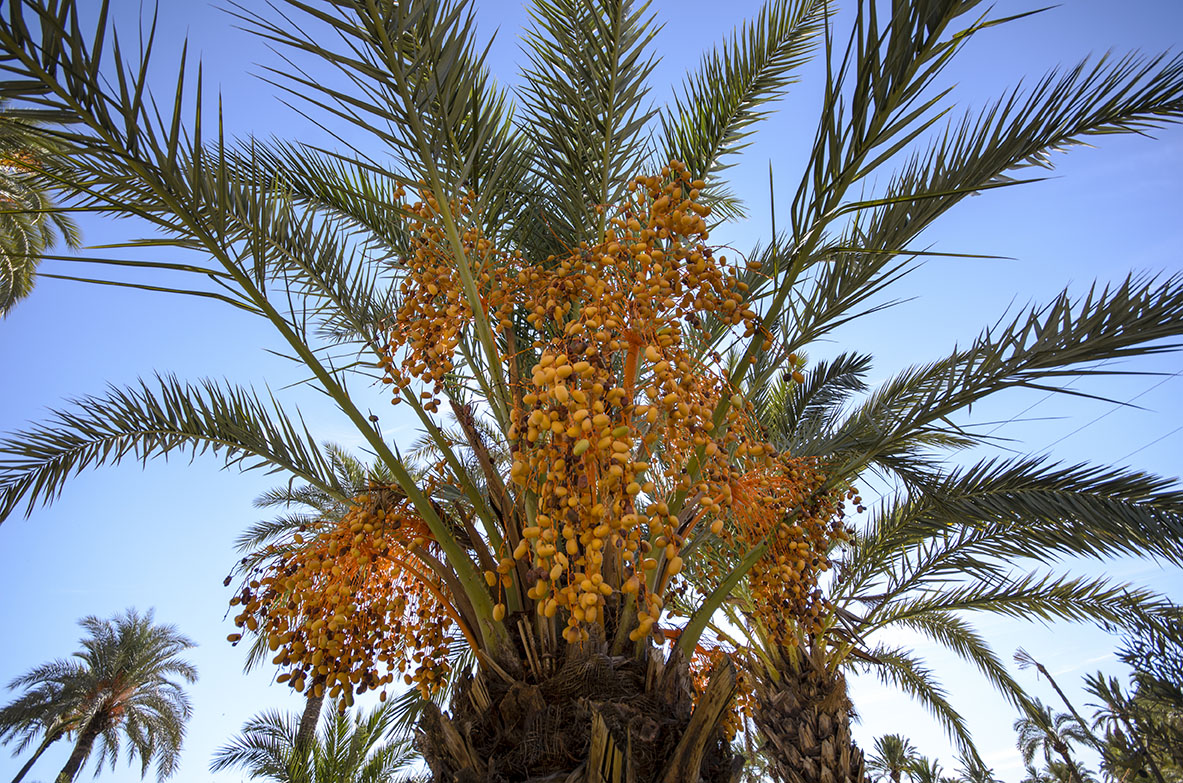
The protagonists
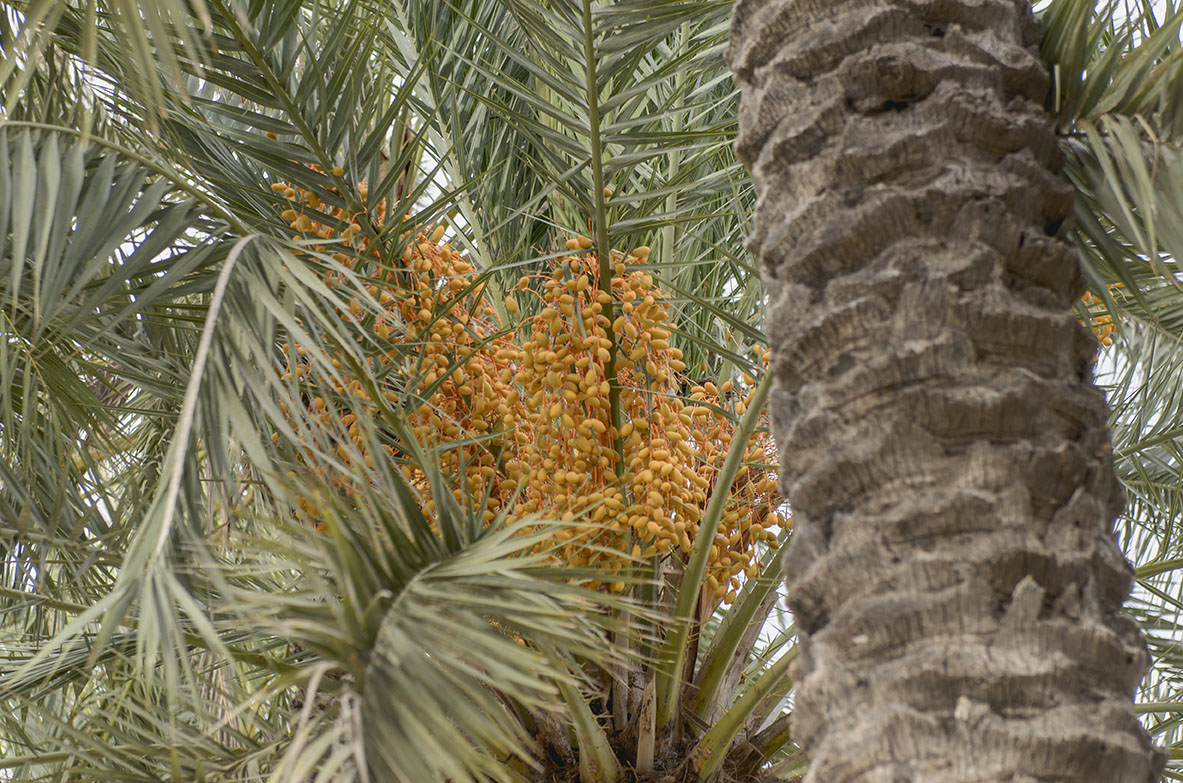
The number of trees in the palm grove has gradually decreased over time. A few decades ago there were about 30,000 palm trees, in 1993 8100 trees were accounted for and in 2002 there were 7400. The inventory update in 2020 showed that there are now 8.931 trees, 5.932 of which are owned by the town council. It is an old palm grove that must be rejuvenated with new plantations. The fact that that 1275 palm trees (517 are owned by the town council) are considered to be monumental trees according to the Law on Heritage Trees of the Valencian Community, because they are over 12 metres tall. 26 of them are “select” palm trees that are distinguished for their special genetic traits, the quality of their fruit, their general appearance, morphology, pollen quality, etc. and they are identified by means of a wooden sign on the stipe that states their name.
Traditional cultivation
The main traditional cultural tasks involved in growing the palm tree are:
Multiplication: by means of seeding or by transplanting specimens that germinate spontaneously or the offshoots that grow in the adventitious roots. Irrigation: the graduated terraces were watered, which normally provided the land with more water in the summer. Fertilizing: fertilizer, namely manure, was scattered on the soil in the palm grove, just like in the rest of the fertile irrigated land of the area. Between four and six carts of manure were used per tahulla (unit of agricultural land that is equivalent to 1118 square meters). (1 cart is the equivalent of 50 “capasos” baskets). Pruning or trimming the palm trees: Traditionally the date palms were pruned in the summer but nowadays due to the red palm weevil plague they have to be pruned in the winter.
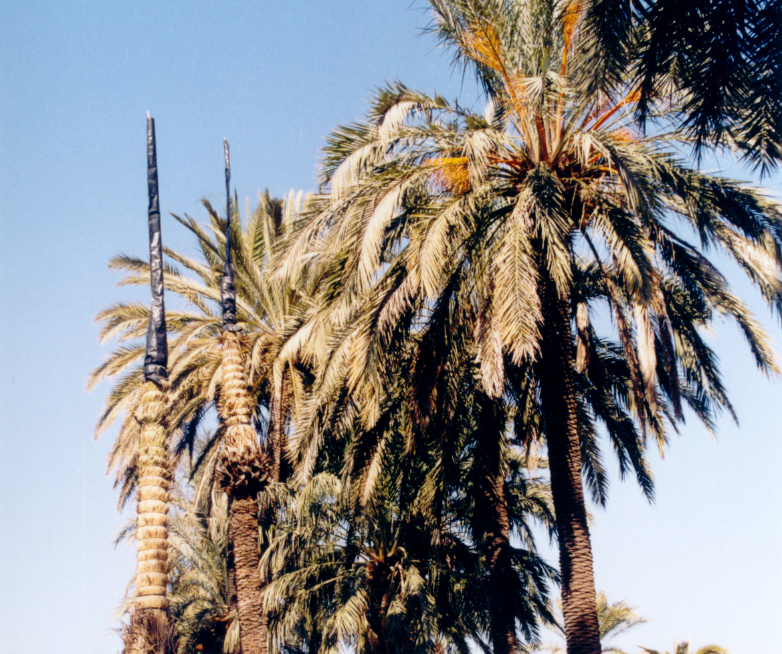
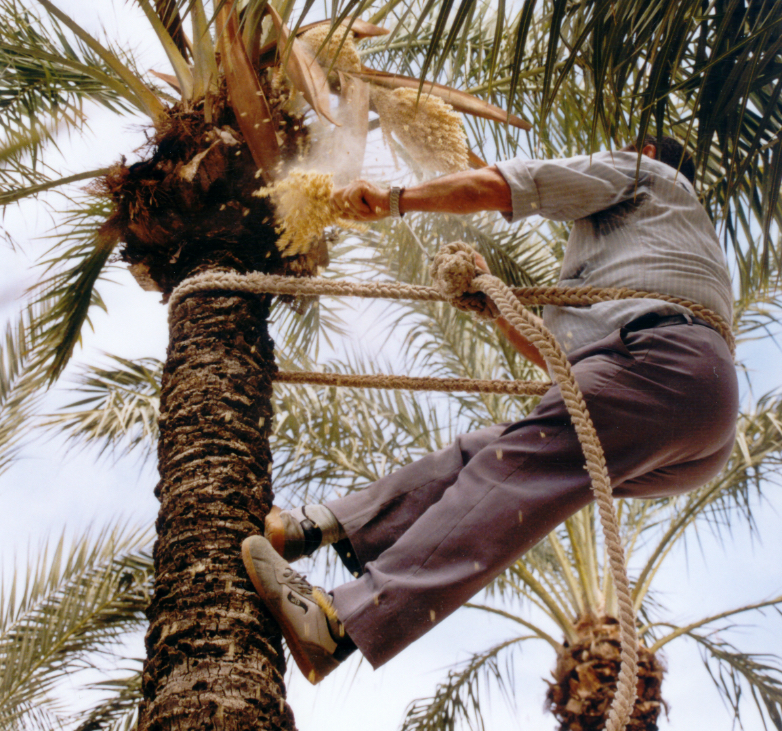


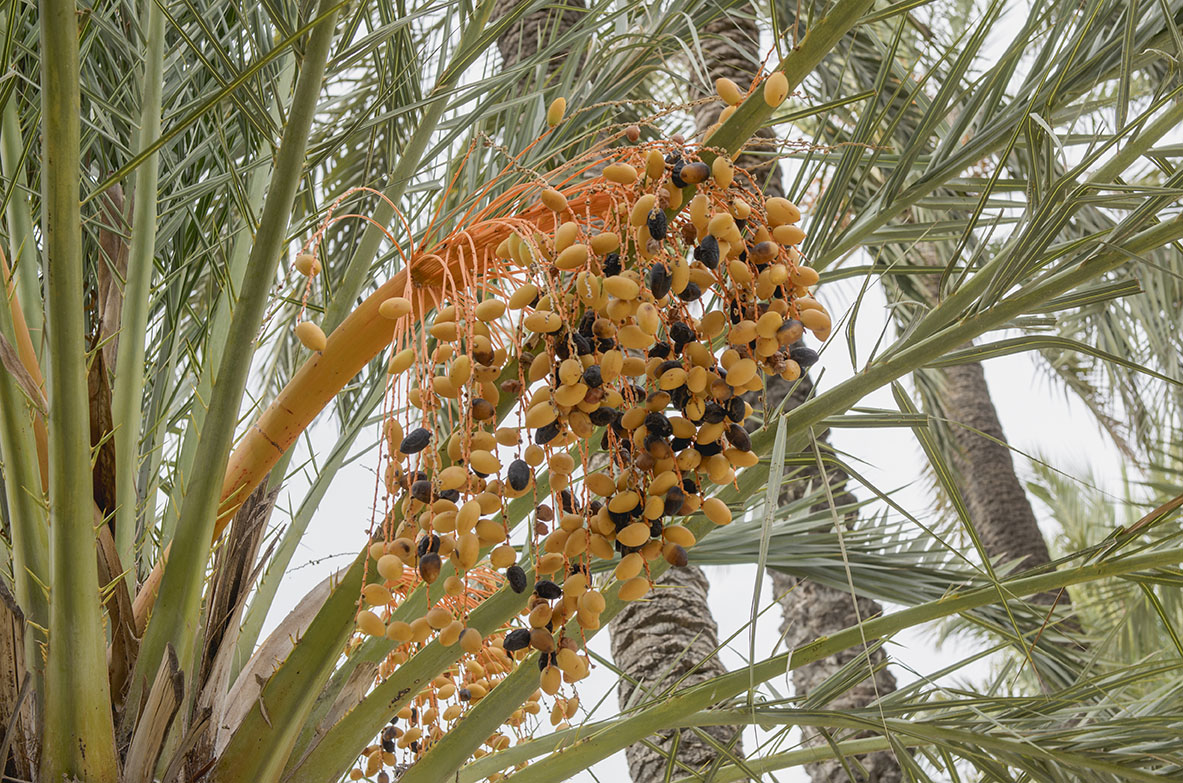
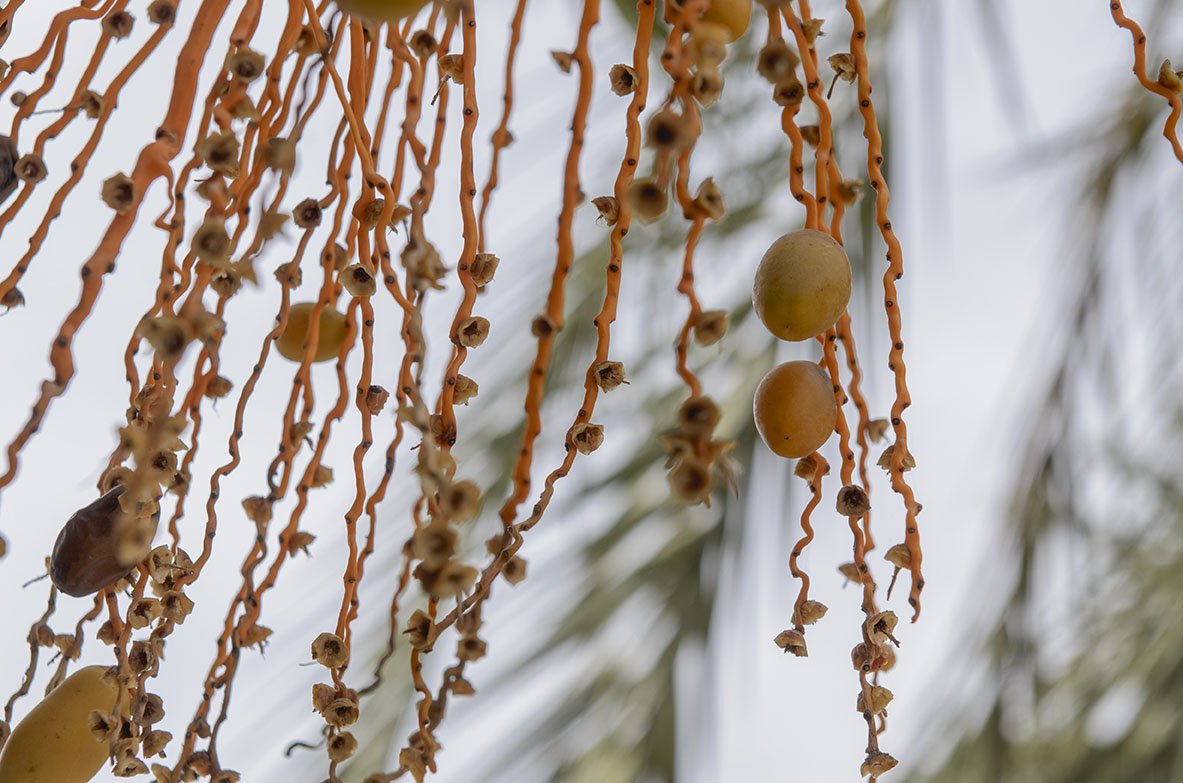
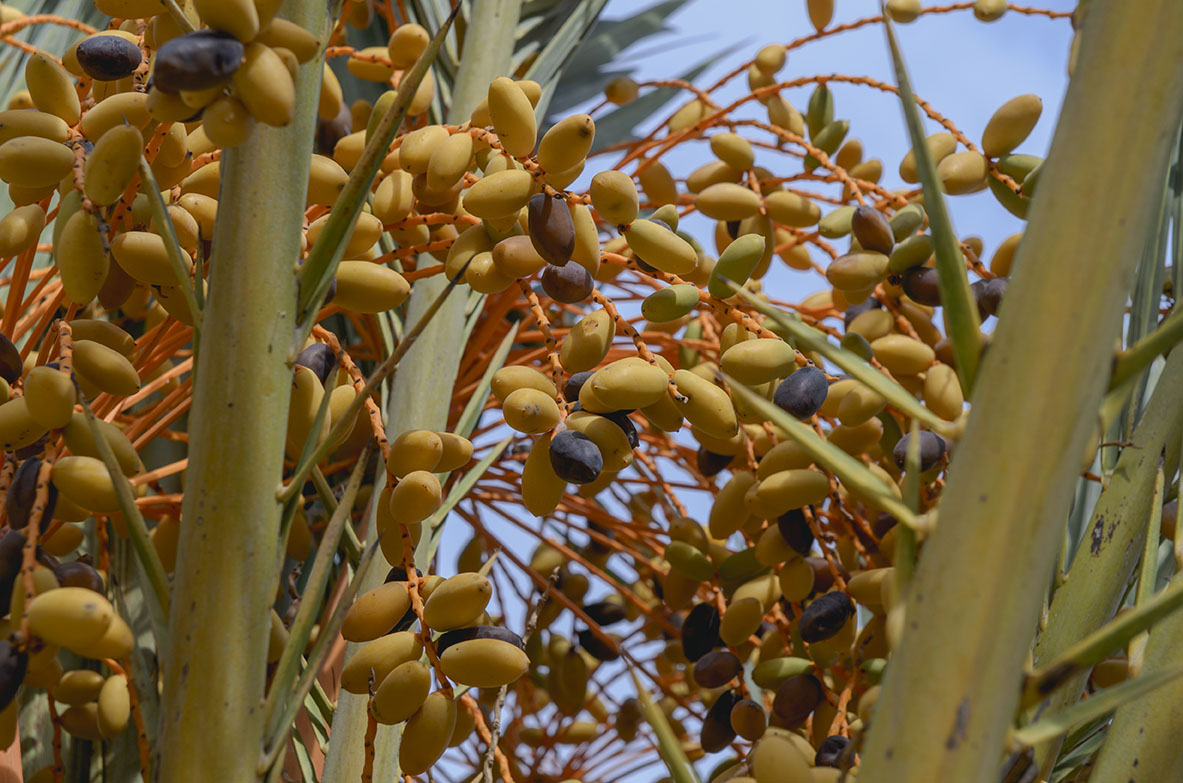
Artificial pollination: is one of the main operations involved in growing the palm trees. This artificial fertilization is achieved by sprinkling the pollen on the female inflorescence, which therefore guarantees a good crop of dates. Harvest: The dates are collected when they are still green if they are going to be pickled and from September onwards when they are ripe, if they are going to be eaten fresh. Hooding: This consists in tying the leaves of the palm tree together and covering them with dried palm leaves, which deprives them from sunlight, so that they don’t go green. This is normally done to unproductive male and female palm trees that are used for the “white palm fronds”, which are crafted into intricate designs and used for on Palm Sunday.
Uses of the palm tree
The stipe was used in traditional architecture as timber and to make benches. The dates are used for human consumption, either raw when they have been left on the trees to ripen (“candíos”) or pickled in vinegar. The palm heart or the tender bud of the stipe of the palm tree, is another culinary delicacy, which is traditionally eaten raw during the celebrations of the saints’ days of San Antón and San Sebastián.
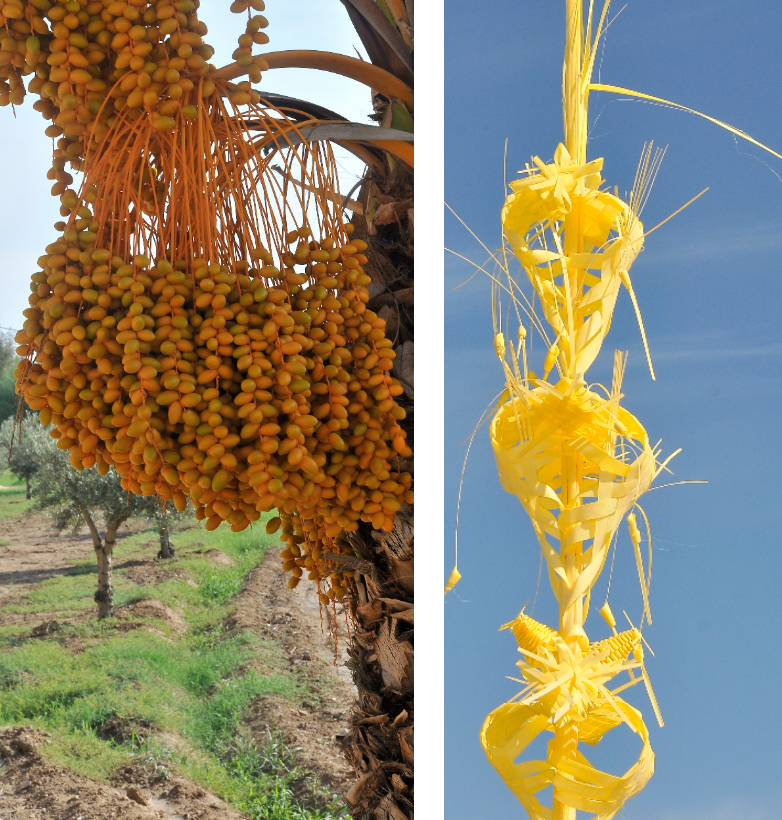


The dead or unhealthy fronds that are pruned were used to build fences and shelters and even small palm tree huts. Once the fronds were cut into strips they could also be used to make brooms. One of the most important traditional uses is the white palm frond. This involves “hooding” or covering the fronds of the palm tree to deprive them of sunlight so that they do not go green, then they can be bleached with sulphur and crafted into intricate designs for Palm Sunday.
The fronds that were not entirely bleached in the aforesaid process were used to make baskets, bassinets and hats.